Microwave ablation technique achieves the treatment purpose by heating up the tissue to coagulate, dehydrate and necrotize. At the same time, the inactivated tumor tissue can produce heat shock protein, an immune system stimulus, to improve the immune function and inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. It is one of the characteristic techniques carried out in Minimally Invasive Intervention Department of Guangzhou Royallee Cancer Center.
What is microwave ablation?
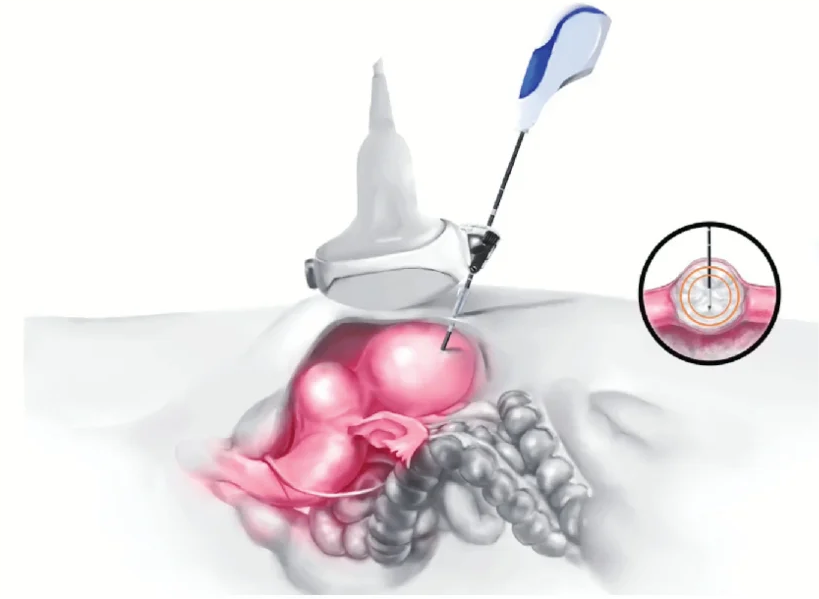
A specially designed microwave ablation needle will puncture the central area of the tumor through the skin. Then it releases microwave magnetic field that causes the surrounding molecules to rotate and move at high speed to generate a large amount of heat, which leads to instant thermal coagulation and necrosis of the tumor. At the same time, the inactivated tumor tissue can produce heat shock protein, an immune system stimulus, to improve the immune function and inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells. The microwave ablation technique of Guangzhou Royallee Cancer Center has the advantages of high thermal efficiency, fast temperature rise and homogeneous thermal field.
Competitiveness of microwave ablation
The skin incision is tinier than that of open surgery, so it does zero damage to the surrounding normal tissues and causes less pain to patients. Microwave ablation applies to a wider range of people, including the elderly, the frail and those with certain diseases that are unable to withstand systemic anesthesia in conventional surgery. Microwave ablation features less trauma and faster recovery, making it an exceptionally good choice for older and weaker patients. Tumors with a single lesion smaller than 5 cm can be necrotized in a 15-minute single procedure.
Unlike conventional radiotherapy and chemotherapy, microwave ablation eliminates tumor lesions without damage to surrounding normal tissues. Thus there is zero toxic side effects and low recurrence rate.
Indications of microwave ablation