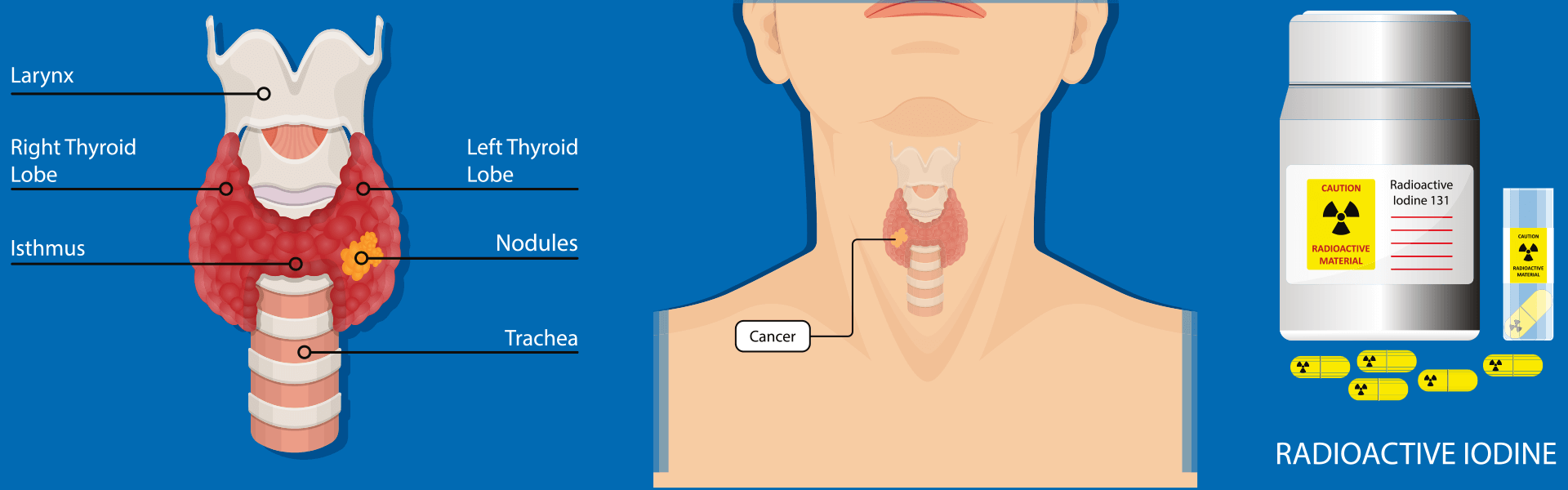
According to China's "Guidelines for the Treatment of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Iodine-131 (2021 Edition)", a considerable number of DTC patients need to receive iodine-131 treatment after surgery.
Principles of iodine-131 technology in treating differentiated thyroid cancer
131I therapy involves oral administration of 131I solution or capsules. The 131I enters the bloodstream through the digestive system, targeting and concentrating residual thyroid cells and residual thyroid tumor cells. Through decay, it emits beta rays, causing edema, degeneration, and necrosis in the target cells. This eliminates the remaining thyroid and cancerous lesions, thereby reducing tumor recurrence and metastasis. The average range of beta rays within tissue is less than 1 mm, and nearly all of their energy is released within the residual thyroid tissue or metastatic lesions, with minimal impact on surrounding normal tissues and organs.
Indications for 131 I treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer
Tumor lesion diameter > 1 cm
Tumor tissue invades the thyroid capsule ( such as infiltrating the fat tissue around the thyroid gland, surrounding the recurrent laryngeal nerve, etc. )
The tumor tissue shows highly invasive pathological subtypes (such as solid subtype, tall cell subtype, etc.), or is accompanied by vascular invasion, BRAFV600E gene mutation, etc., which are closely related to invasiveness and poor prognosis
With cervical lymph node metastasis or distant metastasis
Abnormally elevated serum Tg
If the thyroid tissue has been completely removed, 131I ablation can be performed to facilitate follow-up . After the residual thyroid tissue is removed, follow-up can be performed using Tg testing and whole-body imaging to detect recurrence and metastasis of differentiated thyroid cancer, simplifying follow-up examinations.
Technological advantages
Precision : Use beta rays to precisely eliminate residual thyroid and cancer foci
Safety : minimal impact on surrounding normal tissues and organs
Simple : Oral medication, no need for further surgery


 (+86)18613012387
(+86)18613012387 info@royallee.cn
info@royallee.cn EN
EN CN
CN TH
TH IDN
IDN  AR
AR