The latest data showed that 8 persons were diagnosed with cancer per minute! How to prevent cancer scientifically in 2022?
Statistically speaking, everyone is at risk of developing cancer in their lifetime. Some factors such as increasing age, poor lifestyle habits and changes in the surrounding environment (increased carcinogens) can lead to an increased risk of cancer.
The latest cancer statistics from “Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China, 2016” released by Journal of the National Cancer Center in 2022 showed that more than 8 persons were diagnosed with cancer per minute.
Based on the latest cancer data showing that the cancer has become a common disease, discussion on how to prevent it is made over here.
One basic information
In 2016, there were 4.064 million new cancer cases in China, including:
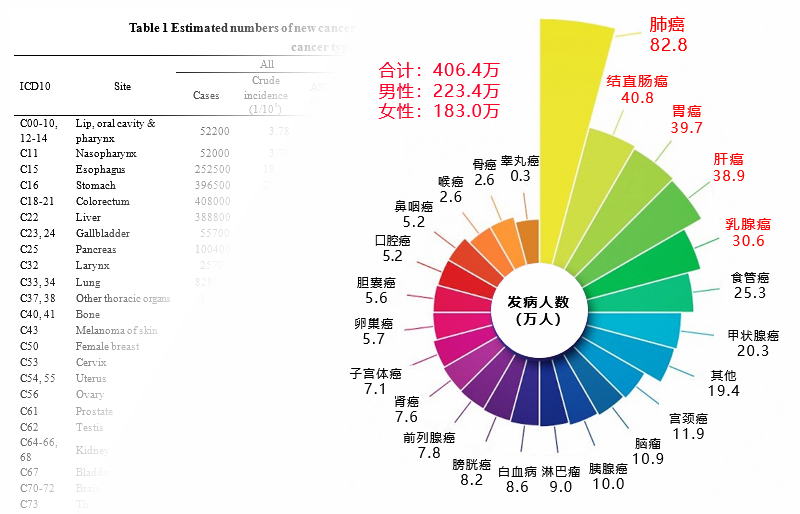
* The graph is taken from “Number of New Cancer Cases and Deaths in China in 2016”
The above graph showed that the rate of new cases in men has been slightly higher than in women since 2016. Among them, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, and breast cancer are still the common high-incidence cancers in China.
It is worth noting that breast cancer in women has surpassed lung cancer as the most common cancer.
Two important differences
Based on the report released by Journal of the National Cancer Center, there are two key differences between male and female in the incidence and prevention of cancer:
1. Age
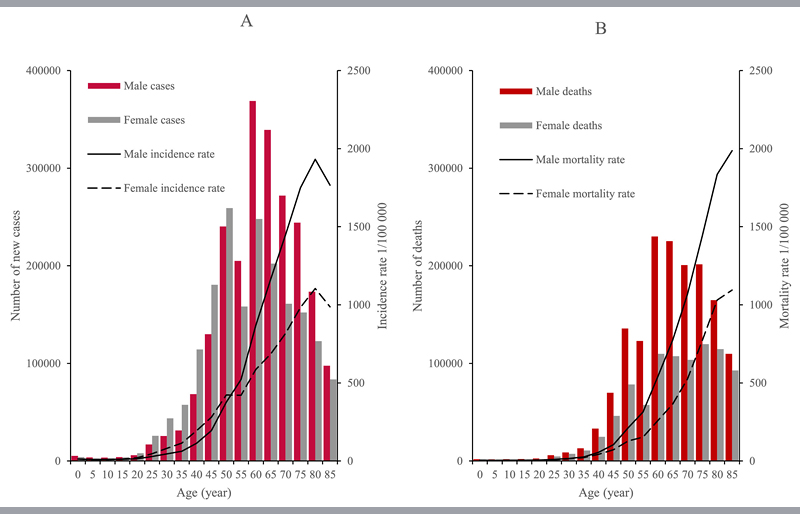
* The graph is taken from “Number of New Cancer Cases and Deaths in China in 2016”
It is generally believed that the peak of new cancer cases in both male and female is between the ages of 60 and 79.
However, the incidence in males aged 0-19 and over 60 was higher than in females, and the incidence in females aged 15-59 was higher than in males.
2. Five different controllable risk factors
In order to highlight the important role of cancer prevention, the World Health Organization (WHO) raised the proportion of preventable cancers from 1/3 to 40%. The National Cancer Center found that 45.2% of cancer deaths were attributed to the behavior, diet, metabolism, environment and infection after analyzing the controllable risk factors for 23 kinds of cancer. Among them, the male incidence accounted for 51.2%, and the five major risk factors were smoking, HBV infection, low intake of fruit, drinking and PM2.5; the female incidence accounted for 34.9%, and the five major risk factors were low intake of fruit, HBV infection, smoking (especially second-hand smoke), overweight and HPV infection.
Three actions that should be kept in mind:
early screening/early diagnosis / early treatment
Physical examination is of great significance for realizing early screening, early detection and accurate diagnosis, formulating personalized treatment plans, performing standardized tumor treatment, and achieving the whole-process management of tumor patients.
Four abnormalities that should be kept eyes on:
Eleven symptoms mentioned on “Guidelines for Cancer Prevention and Screening (Popularization of Science)” published by Journal of the National Cancer Center in 2021 are regarded as the warning signs of cancer, referred to as cancer “alarm whistle”.
1. Skin changes
Lumps on the body surface
Unhealed ulcers on the skin or mucous membranes
Black moles or warts that darken or grow rapidly in a short period of time
2. Digestive tract changes
Persistent indigestion and loss of appetite;
Changes in bowel habits and stool traits or bloody stool;
3. Genitourinary system changes
Painless hematuria, dribble urination;
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, especially contact bleeding;
4.Others
Hearing abnormalities, nasal hemorrhage, headache;
Persistent hoarseness, dry cough, blood in sputum;
Uncomfortable feelings, such as obstructive dysphagia, pain;
Unexplained fever, fatigue, progressive weight loss.
Five screenings that should be kept
Eleven symptoms mentioned on “Guidelines for Cancer Prevention and Screening (Popularization of Science)” published by Journal of the National Cancer Center in 2021 are regarded as the warning signs of cancer, referred to as cancer “alarm whistle”
Screening method:
Gastroscopy and gastric biopsy are the most authoritative methods for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Target population for early gastric cancer screening
According to “Consensus Opinion on Early Gastric Cancer Screening and Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment in China (2014)” and “Expert Consensus on Screening Process for Early Gastric Cancer in China (draft) (2017)”, those who are over 40 years old and meet any of the following are recommended to undergo gastric cancer screening.
• People in areas with high incidence of gastric cancer
• People with helicobacter pylori infection
• Immediate family members of gastric cancer patients;
• Presence of risk factors for gastric cancer (such as high salt diet, pickled food, smoking, heavy drinking)
• Past precancerous gastric diseases such as atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric polyps, post-operative gastric remnant, hypertrophic gastritis, and pernicious anemia.
Breast cancer
“Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China, 2016” showed that Both overall and age-standardized mortality rates for female breast cancer were on the rise.
Screening method:
• Color Doppler ultrasound of breasts has a high diagnostic rate for cysts, solid tumors and dense breast masses.
• X-ray of breast (mammography) has a high diagnostic rate for early breast cancer.
Inter-cut
In recent years, with the care for females’ health and the increasing awareness of health, two cancer screenings have been included in the free inspection program.
Our hospital has officially become a designated institution for free “two cancers” screening in Huangpu district since April 2022, targeting females aged 35~64 with registered permanent residence in Longhu Street. Females who are interested in screening can ask the sub-district/neighborhood committee for details and register on the registration form.
Colorectal cancer
Compared with 2015, the incidence of colorectal cancer has further increased, the number of new cases has risen to the second place, and the number of cancer deaths has climbed to the fourth place.
Early screening method:
• FIT once a year
• FIT-DNA once a year or once every 3 years
Colonoscopy to the ileocecum
Target population for colorectal cancer screening
• Males
• Those aged over 45
• Smokers
• Body mass index ≥ 24, BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height (m)²
Liver cancer
Liver cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in China. At present, the cause and pathogenesis of primary liver cancer are still unknown. According to relevant investigations and studies, it is related to alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis, food and drinking water, poisons and parasites, and genetic factors.
Screening method:
• API test is a specific marker for hepatocellular carcinoma.
• Ultrasound of abdomen can detect suspicious intrahepatic lesions early and sensitively, accurately identify cystic or solid lesions, and observe whether there are other metastases in the liver or abdomen.
Target population for liver cancer screening
Males aged 45-74 and females aged 50-74 with any of the following conditions are at high risk of liver cancer:
• Positive HBsAg
• HCV infection
• Past history of liver cirrhosis or family history of liver cancer
Lung cancer
A report showed that the number of lung cancer deaths in China would be as high as 710,000, accounting for 23.8% of the total cancer deaths. One out of every five patients who die from cancer succumbed to lung cancer.
Screening method:
National Lung Screening Trial, NLST showed that Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) can reduce the risk of death by 20% compared with conventional chest X-ray in people at high risk of lung cancer.
Target population for lung cancer screening
• Smokers with over 30 packs of cigarettes per year
• Those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
• Those with a history of occupational exposure for at least 1 year
• Passive smokers for over 20 years, including those who have smoked more than 30 packs of cigarettes per year and quit smoking for less than 15 years.
