Breast cancer, commonly known as the "pink killer," is a prevalent malignant tumor that poses a significant threat to women's health. However, many women do not pay enough attention to it. So, who is at a higher risk of developing breast cancer? How can the general population detect breast cancer, and what measures can be taken for its prevention?
 Who is at a higher risk of developing the disease?
Who is at a higher risk of developing the disease?
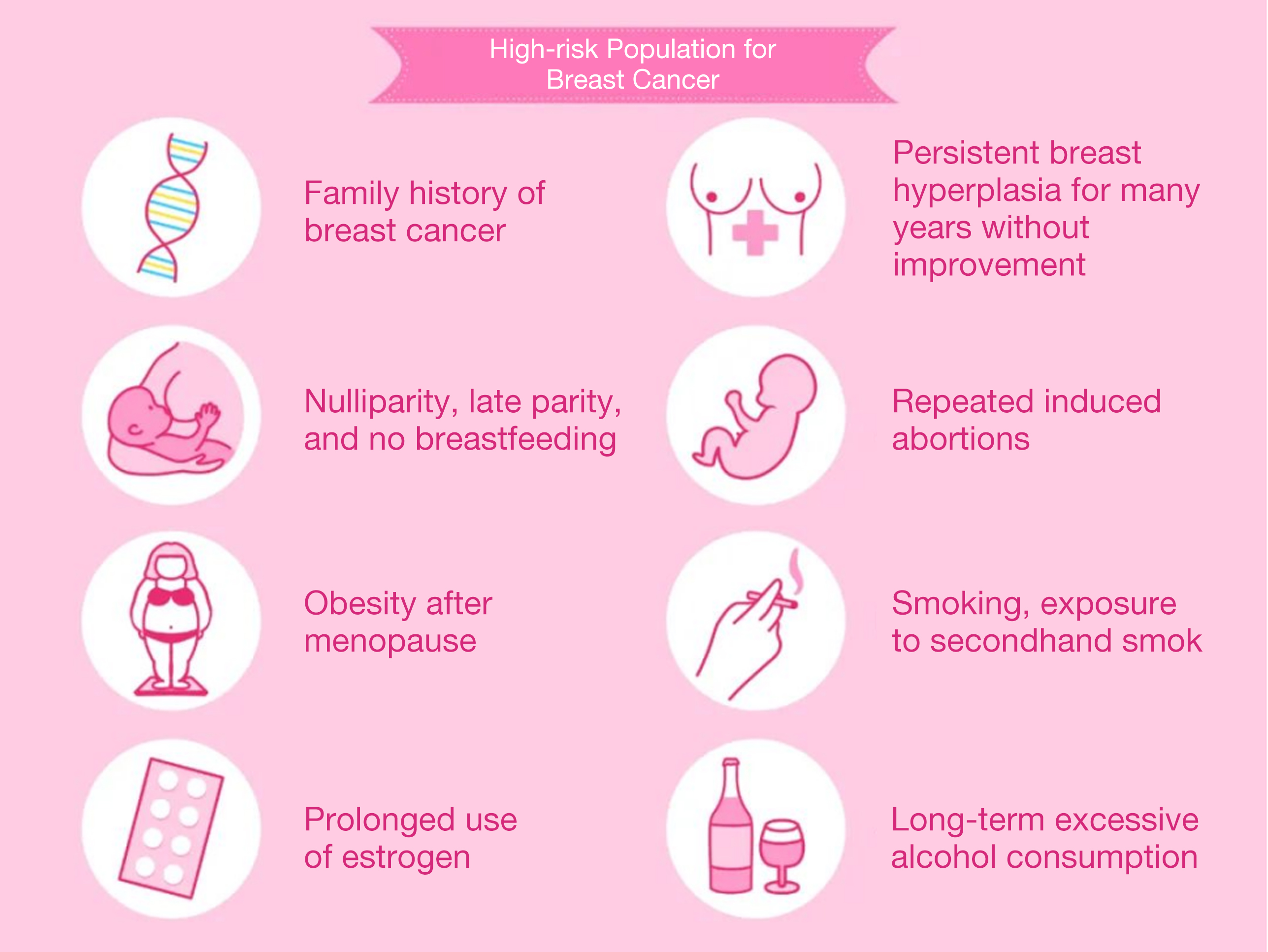
1. Population with breast nodules, especially those with malignant breast nodules;
2. Certain genetic mutations, such as the BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancer susceptibility genes;
3. Family history, referring to a history of cancer in first or second-degree relatives. First-degree relatives include parents, siblings, children, and second-degree relatives include grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, etc.;
4. If the individual has had breast cancer before, the probability of the other breast being affected is more than four times higher;
5. Age over 65 years old.
 How to Detect Breast Cancer?
How to Detect Breast Cancer?
The detection of breast cancer primarily relies on regular self-examinations and routine scheduled medical check-ups.
1. Regular Self-Examination
It is recommended that female friends master the method of self-examination for breast health, cultivate the habit of regular breast self-checks, actively undergo breast cancer screenings, and prevent potential risks.
Specific Method:
After the end of menstruation, on days 7-10, stand in front of a mirror with hands hanging down. Carefully observe whether the size of both breasts is symmetrical, if there are any changes in shape, if the nipples are retracting, if there is any discharge, and if the breast skin is intact.
Next, use the four fingers together to slide over the breast in a circular motion, checking for any lumps. Slide from the upper outer side to the lower outer side, then from the upper inner side to the lower inner side, all the way to the nipple.
Finally, compare and check for any lumps under the armpits on both sides.
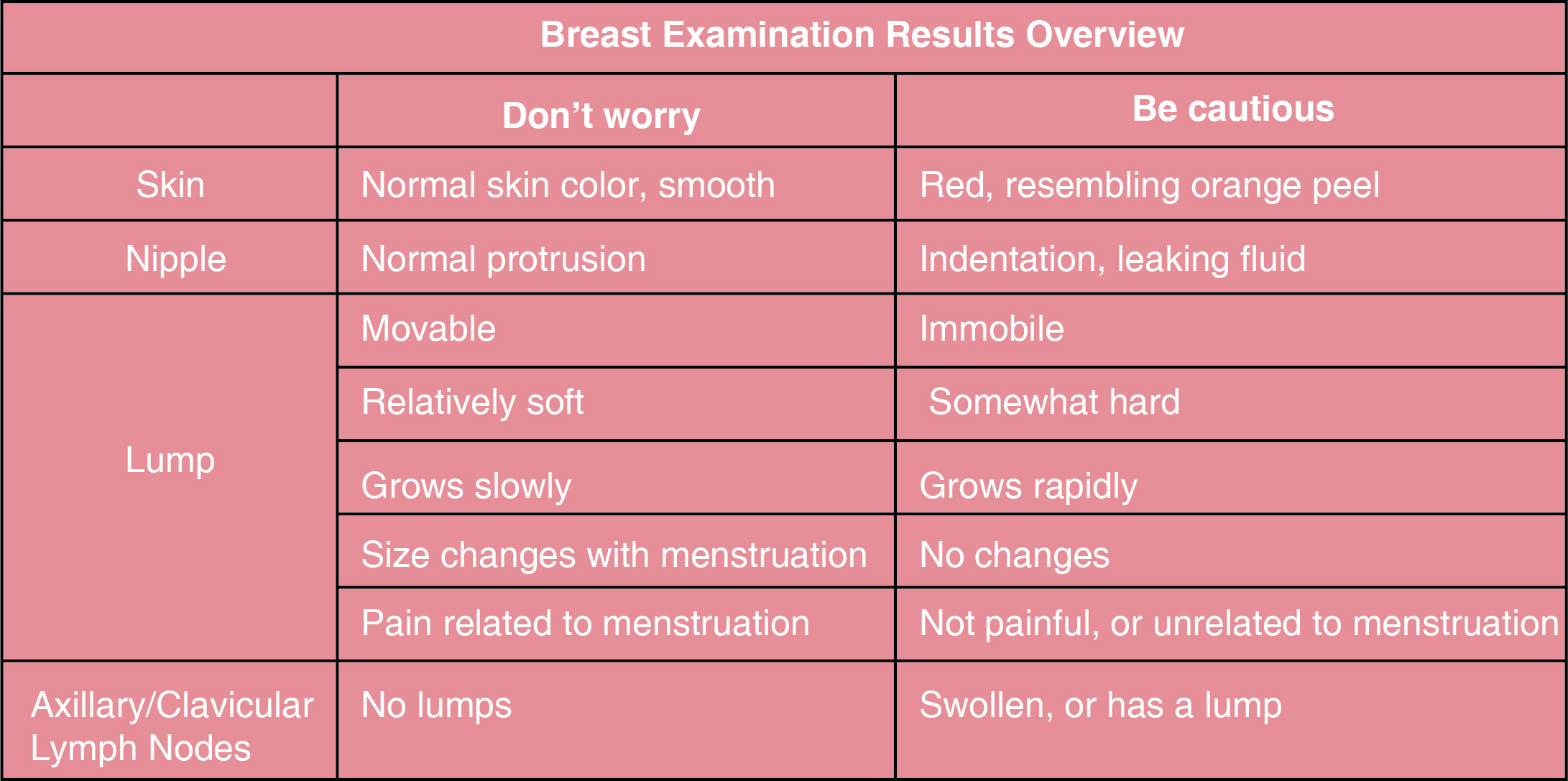
If you notice any abnormalities during self-examination, it is advisable to promptly visit a hospital for examination and seek timely diagnosis and treatment.
2. Regular Physical Examinations
In our country, the peak age for the onset of breast cancer in women is 45-54 years old, which is about 10 years earlier than in European and American countries. Therefore, the guidelines in our country suggest that the starting age for breast cancer screening for the general population at normal risk is 40 years old. However, for individuals at high risk of breast cancer, the starting age for screening can be advanced to before the age of 40.
Currently, common methods for breast examination in China include mammography (mammogram), ultrasound examination, ductoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and PET/CT.
For individuals under 40 years old or those without high-risk factors: In addition to regular self-examination, ultrasound examination is generally recommended as the primary method, with a suggestion of at least once a year.
For individuals aged 40 and above or those at high risk for breast cancer: It is recommended to add mammography every 1-2 years to the routine, in addition to regular ultrasound examinations.
For women at high risk of breast cancer: Supplementary breast MRI examination is also required.
Adding mammography and MRI examination can increase the detection rate of small lesions, enhance the early detection of breast cancer, and significantly improve the cure and treatment effectiveness of breast cancer.
 How to Prevent Breast Cancer?
How to Prevent Breast Cancer?
1. Maintain a healthy diet, reduce high-fat intake appropriately.
Higher fat intake may trigger breast cancer, which is related to excessive fat intake leading to increased endogenous estrogen secretion. Studies show that individuals adhering to a low-fat diet can reduce the risk of breast cancer by about 9%. Moderately reducing fat intake can help prevent breast cancer.
2. Quit smoking, control alcohol consumption, or avoid alcohol altogether.
Epidemiological studies suggest that alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing breast cancer. If an additional 10 grams of alcohol is consumed daily, the relative risk of breast cancer will increase by 7%.
3. Consume more vegetables and fruits.
Since the 1990s, various studies have consistently shown that individuals who consume more vegetables and fruits have a lower risk of developing cancer. A 2012 meta-analysis indicated that a higher intake of fruits, berries, and vegetables can reduce the risk of breast cancer by approximately 41%.
4. Maintain a cheerful mood.
Depression, anxiety, and other emotions can increase fat embolism levels. Maintaining an optimistic and relaxed mindset is crucial for breast health.
5. Engage in regular moderate exercise.
Women who exercise regularly have a 30% lower chance of developing breast cancer compared to those who don't. Regular exercise not only benefits overall health but also helps prevent the occurrence of breast cancer.
 Quick Tip: Pay attention to their breasts
Quick Tip: Pay attention to their breasts
While 99% of individuals with breast cancer are females, unfortunately, 1% falls on men. Therefore, besides being mindful of one's own breast health, it is also important to pay attention to the breasts of close male relatives such as fathers, husbands, and sons. If there is a painless lump with a relatively hard texture and unclear boundaries in his chest, inwardly retracted nipples, or discharge, be sure to go to the hospital for timely examination.
 Who is at a higher risk of developing the disease?
Who is at a higher risk of developing the disease?
1. Population with breast nodules, especially those with malignant breast nodules;
2. Certain genetic mutations, such as the BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancer susceptibility genes;
3. Family history, referring to a history of cancer in first or second-degree relatives. First-degree relatives include parents, siblings, children, and second-degree relatives include grandparents, aunts, uncles, cousins, etc.;
4. If the individual has had breast cancer before, the probability of the other breast being affected is more than four times higher;
5. Age over 65 years old.
 How to Detect Breast Cancer?
How to Detect Breast Cancer?The detection of breast cancer primarily relies on regular self-examinations and routine scheduled medical check-ups.

1. Regular Self-Examination
It is recommended that female friends master the method of self-examination for breast health, cultivate the habit of regular breast self-checks, actively undergo breast cancer screenings, and prevent potential risks.
Specific Method:
After the end of menstruation, on days 7-10, stand in front of a mirror with hands hanging down. Carefully observe whether the size of both breasts is symmetrical, if there are any changes in shape, if the nipples are retracting, if there is any discharge, and if the breast skin is intact.
Next, use the four fingers together to slide over the breast in a circular motion, checking for any lumps. Slide from the upper outer side to the lower outer side, then from the upper inner side to the lower inner side, all the way to the nipple.
Finally, compare and check for any lumps under the armpits on both sides.

If you notice any abnormalities during self-examination, it is advisable to promptly visit a hospital for examination and seek timely diagnosis and treatment.
2. Regular Physical Examinations
In our country, the peak age for the onset of breast cancer in women is 45-54 years old, which is about 10 years earlier than in European and American countries. Therefore, the guidelines in our country suggest that the starting age for breast cancer screening for the general population at normal risk is 40 years old. However, for individuals at high risk of breast cancer, the starting age for screening can be advanced to before the age of 40.
Currently, common methods for breast examination in China include mammography (mammogram), ultrasound examination, ductoscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and PET/CT.
For individuals under 40 years old or those without high-risk factors: In addition to regular self-examination, ultrasound examination is generally recommended as the primary method, with a suggestion of at least once a year.
For individuals aged 40 and above or those at high risk for breast cancer: It is recommended to add mammography every 1-2 years to the routine, in addition to regular ultrasound examinations.
For women at high risk of breast cancer: Supplementary breast MRI examination is also required.
Adding mammography and MRI examination can increase the detection rate of small lesions, enhance the early detection of breast cancer, and significantly improve the cure and treatment effectiveness of breast cancer.
 How to Prevent Breast Cancer?
How to Prevent Breast Cancer?1. Maintain a healthy diet, reduce high-fat intake appropriately.
Higher fat intake may trigger breast cancer, which is related to excessive fat intake leading to increased endogenous estrogen secretion. Studies show that individuals adhering to a low-fat diet can reduce the risk of breast cancer by about 9%. Moderately reducing fat intake can help prevent breast cancer.
2. Quit smoking, control alcohol consumption, or avoid alcohol altogether.
Epidemiological studies suggest that alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing breast cancer. If an additional 10 grams of alcohol is consumed daily, the relative risk of breast cancer will increase by 7%.
3. Consume more vegetables and fruits.
Since the 1990s, various studies have consistently shown that individuals who consume more vegetables and fruits have a lower risk of developing cancer. A 2012 meta-analysis indicated that a higher intake of fruits, berries, and vegetables can reduce the risk of breast cancer by approximately 41%.
4. Maintain a cheerful mood.
Depression, anxiety, and other emotions can increase fat embolism levels. Maintaining an optimistic and relaxed mindset is crucial for breast health.
5. Engage in regular moderate exercise.
Women who exercise regularly have a 30% lower chance of developing breast cancer compared to those who don't. Regular exercise not only benefits overall health but also helps prevent the occurrence of breast cancer.
 Quick Tip: Pay attention to their breasts
Quick Tip: Pay attention to their breastsWhile 99% of individuals with breast cancer are females, unfortunately, 1% falls on men. Therefore, besides being mindful of one's own breast health, it is also important to pay attention to the breasts of close male relatives such as fathers, husbands, and sons. If there is a painless lump with a relatively hard texture and unclear boundaries in his chest, inwardly retracted nipples, or discharge, be sure to go to the hospital for timely examination.
